Common staining methods for bacterial staining specimen inspection
The basic procedure of bacterial staining: smear (drying) → fixation → dyeing (primary dyeing → mordant dyeing → destaining → counterstaining). 1. Single dyeing method: Use one dye to dye bacteria and surrounding objects to the same color. After the bacteria are treated by single staining method, their morphology, arrangement, size and simple structure can be observed, but they cannot show the difference in staining of various bacteria. 2. Double dyeing method: The method of dyeing with two or more dyes is called double dyeing method or differential dyeing method. Commonly used are Gram staining and acid-fast staining. (1) Gram stain: This method is the most classic and commonly used staining method in bacteriology. Except for a few specimens such as feces and blood, most specimens are subjected to Gram staining and microscopic examination before separation and culture. Significance: ①Identification of bacteria: All bacteria are divided into two categories of G + bacteria and G- bacteria through Gram stain, which can initially identify bacteria and narrow the scope, which is helpful for further identification. Sometimes combined with the special morphological structure and arrangement of bacteria, the pathogens can be initially identified. ②Select drug reference: G + bacteria and G- bacteria show different sensitivities to some antibiotics. ③Related to pathogenicity: Most of the pathogenic substances of G + bacteria are exotoxins, while most of G-bacteria can produce endotoxins, and the two pathogenic effects are different. (2) Acid-fast staining: Acid-fast staining can also divide bacteria into two categories: acid-resistant bacteria and non-acid-resistant bacteria. Because most of the pathogenic bacteria in clinical are non-acid-resistant bacteria, acid-fast staining is not used as a routine bacterial inspection item in clinical, but only for bacterial inspection of tuberculosis and leprosy. Specimens suspected of being infected with M. tuberculosis can be preliminarily identified by oil staining after acid-fast staining. If the red acid-fast bacilli are found, it can be reported as "find acid-fast mycobacteria". It has important reference value for the diagnosis and treatment of clinical diseases. 3. Fluorescence staining: Fluorescence staining has strong sensitivity, high efficiency and easy to observe the results, and has great practical value in the identification of clinical bacteria. It is mainly used for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Shigella dysenteriae. If the sputum specimen is smeared and fixed, it is stained with the fluorescent dye auramine 0 method (also known as auramine 0-rhodamine B method), and examined with a fluorescent microscope, and golden yellow fluorescent bacteria balls can be observed on a dark background. In addition to the dyeing methods described above, flagella dyeing and metachromatic particle dyeing are also used for bacterial identification.
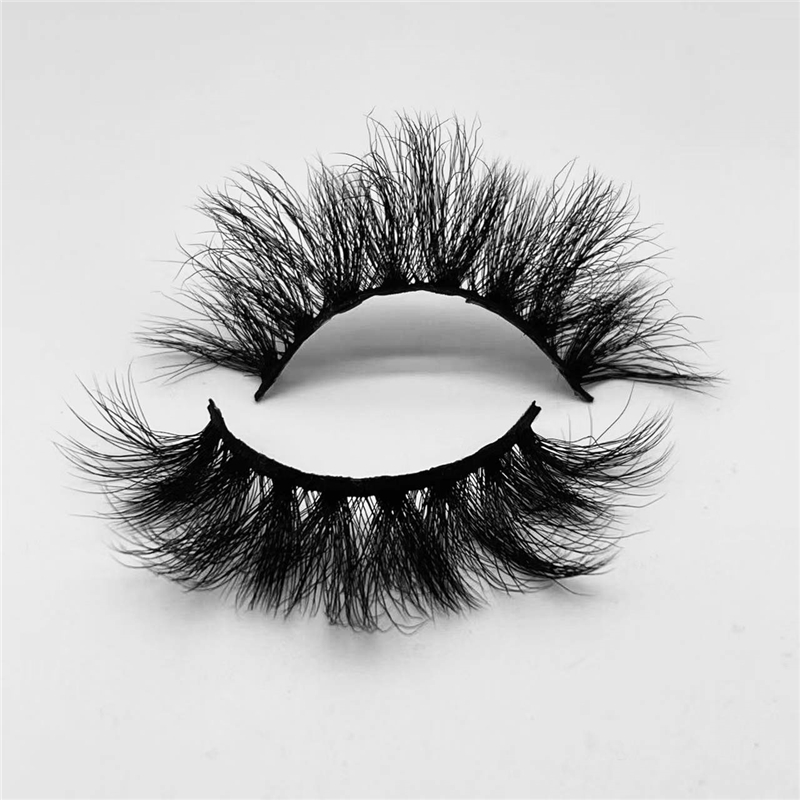
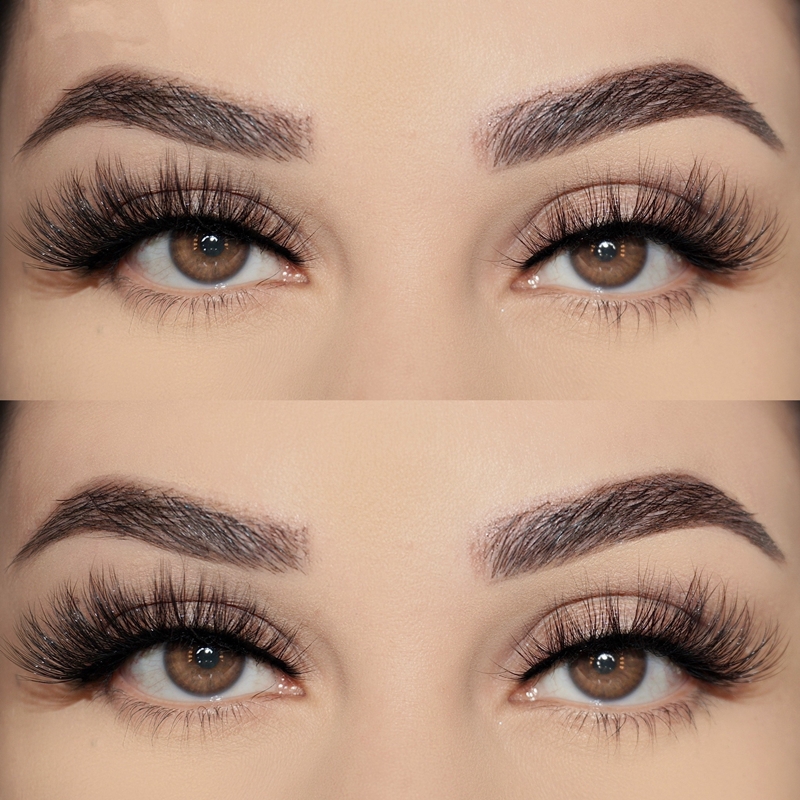
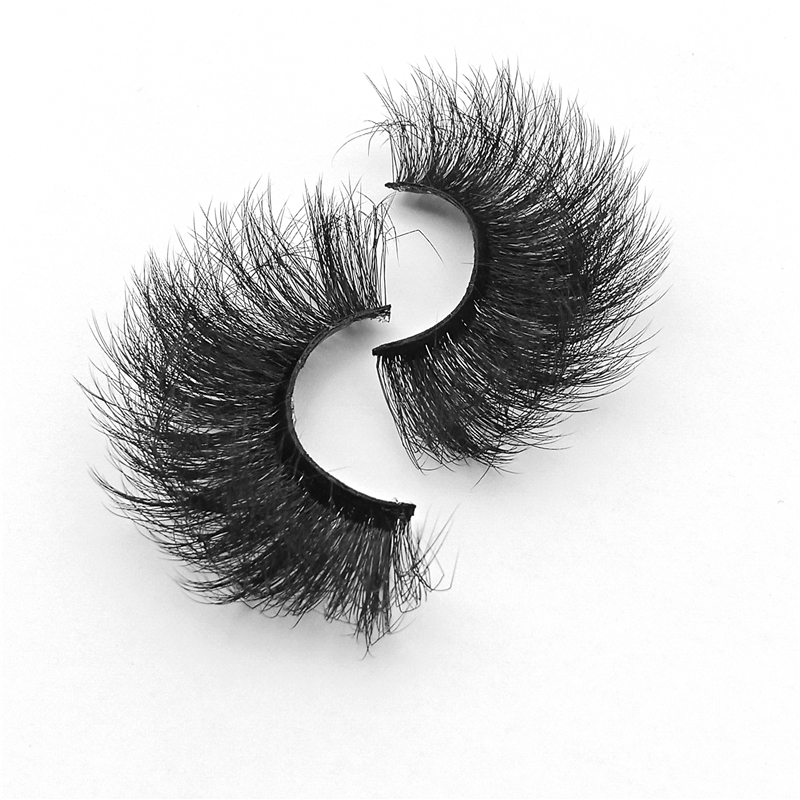
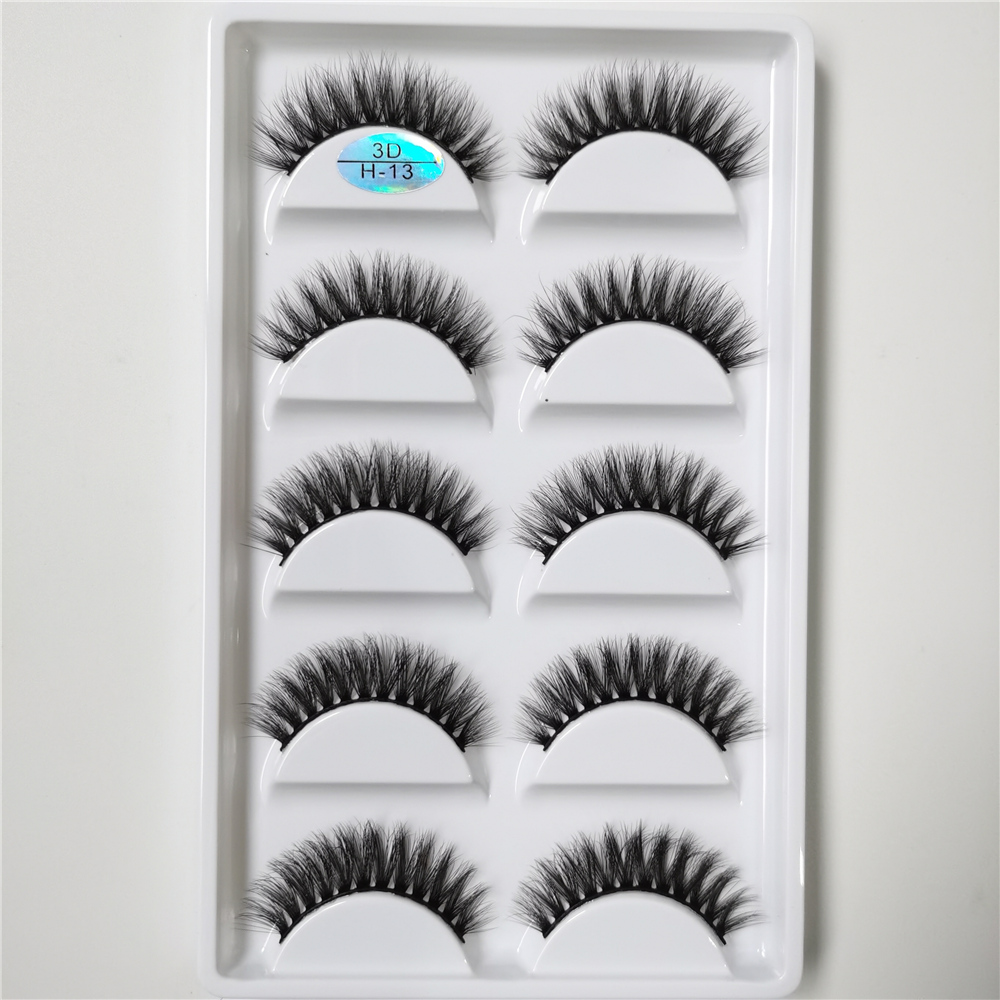
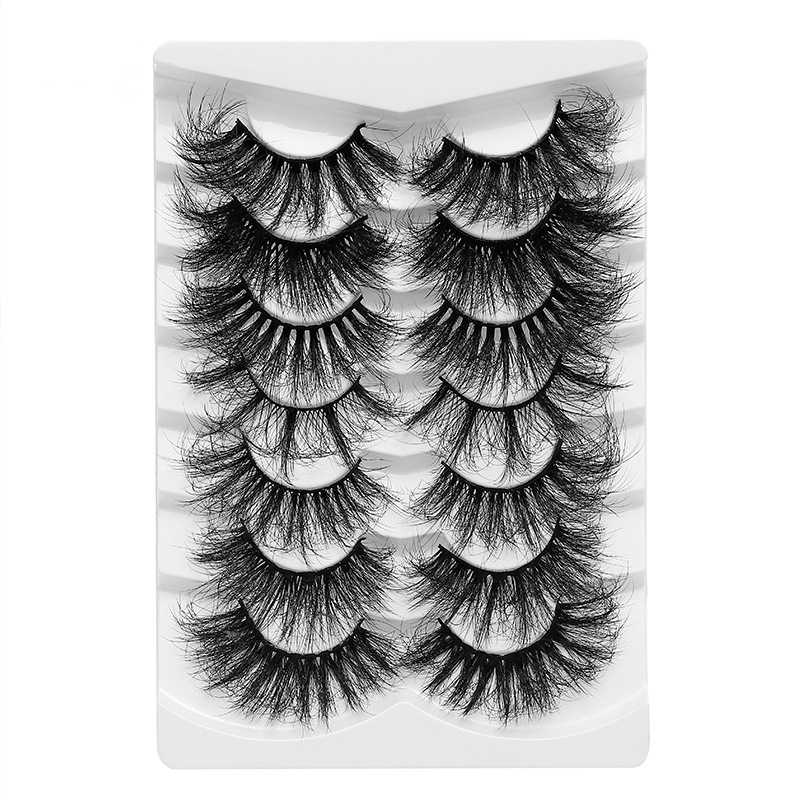
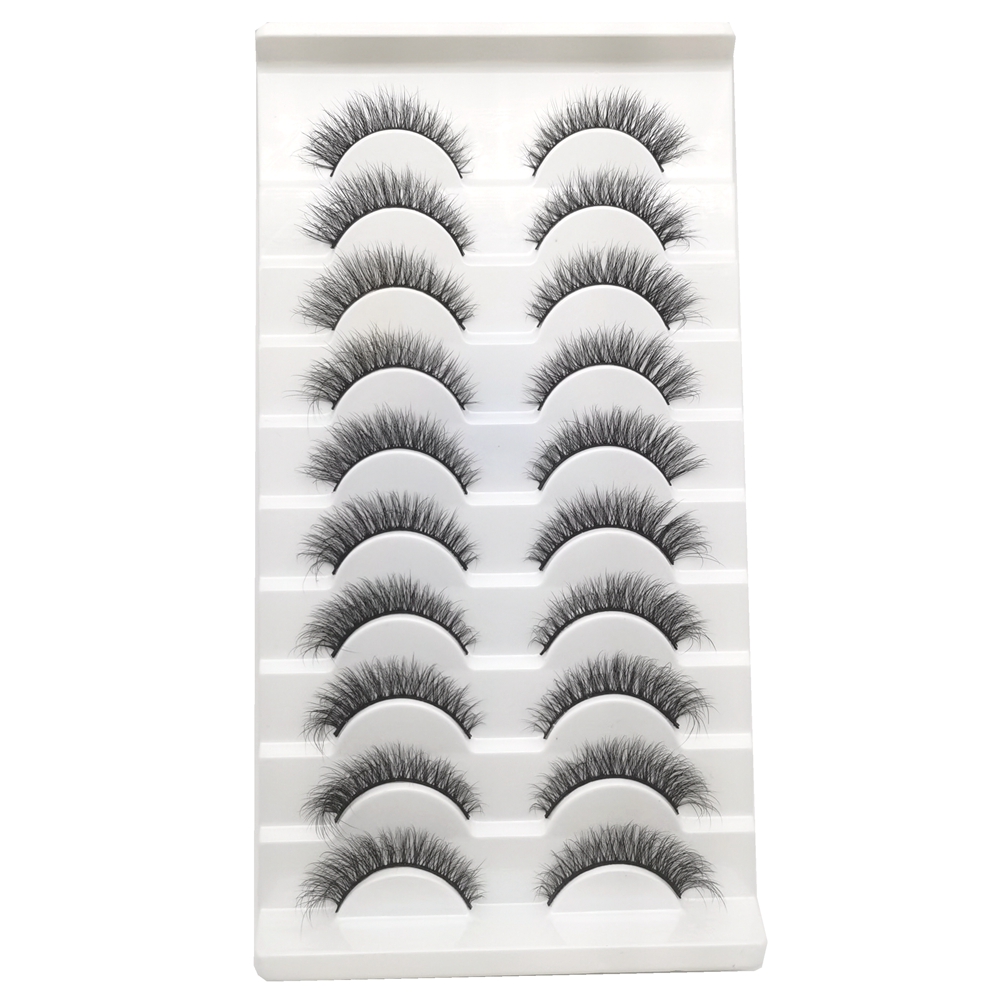
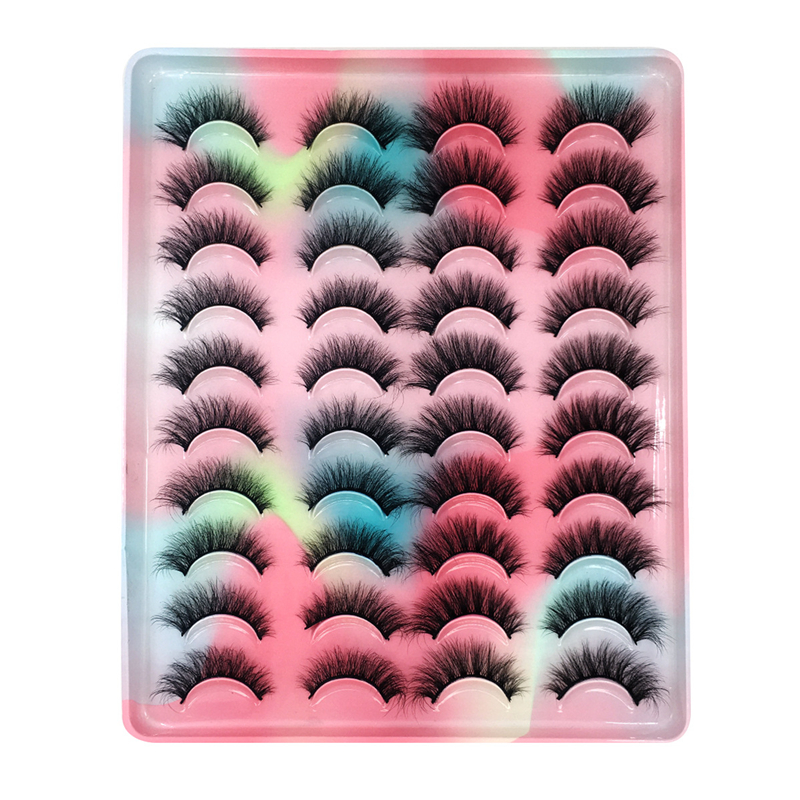
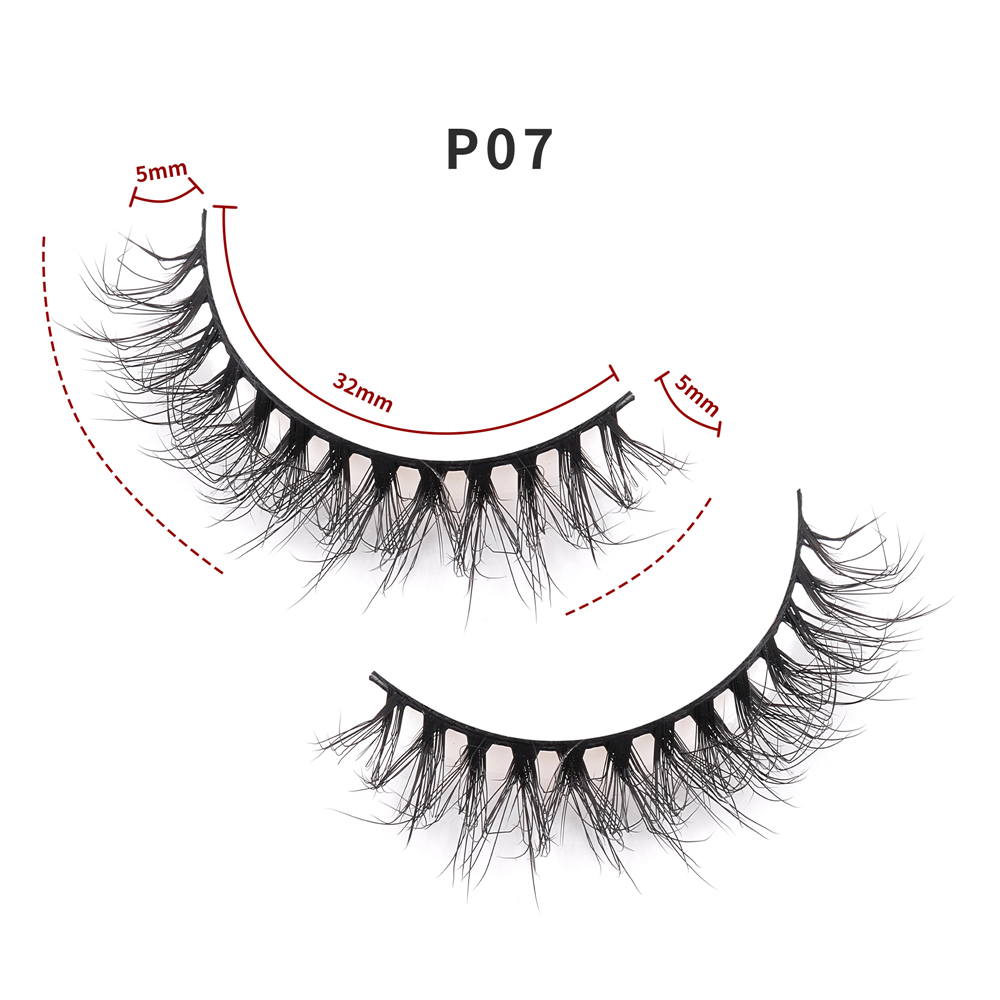
faux Mink Lashes are similar like mink fur lashes but competitive price. as one of popular strip lashes among eye lashes, it is natural looking, soft and handmade. also sell and pack as Lashes Sets . such as 3 pairs lashes, 4 pairs lashes, 5 Pairs Lashes , 7 Pairs Lashes , 10 Pairs Lashes , 16 pairs lashes and 20 Pairs Lashes. these fake eyelashes also have Short Eyelashes, Medium Eyelashes and Long Eyelashes . bellow are some of hot selling samples.
Faux Mink Lashes,Fake Eyelashes,Big Eyelashes,Short Fake Eyelashes Zhengzhou Cuka Electronic Commerce Co., Ltd. , https://www.cukalashes.com