Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is currently attracting widespread attention. Because this technology can be used to track and manage almost all physical objects. Therefore, more and more retailers and manufacturers are concerned about and support the development and application of this technology.
RFID technology was developed by the Auto-ID Center and its application forms are tags, cards, and label devices.
The marking device consists of an RFID chip and an antenna. There are three types of markings: automatic, semi-passive and passive. Basically, passive RFID tags are being developed on the market because they are cheap and easy to configure.
Passive marking devices use radio waves for operation and communication, and the signals must be within the range allowed by the identifier, usually 10 feet (about 3 meters). This type of tag is suitable for short-range information identification, such as a disposable razor or a removable blade box.
RFID chips can be read-only or read/write, depending on the application requirements. The passive marking device uses an E2PROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), which facilitates the writing of data on a specific electronic processing device. The general marking device is set to read-only at the factory. The Auto-ID specification also contains deadlock commands to prevent the tracking process in appropriate situations.
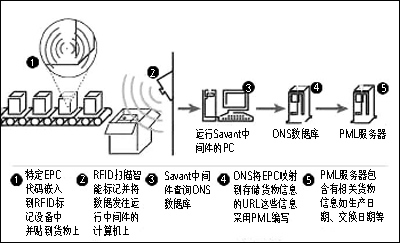
RFID identification working principle
The Electronic Product Code (EPC) specification developed by the Auto-ID Center identifies targets and all target-related data. The EPC system uses the correct database to link to the EPC code, and vendors and retailers can query, manage, and change operations based on permissions.
Once the tag is attached to the product or device, the RFID reader can read the data stored in the tag. Its working principle is shown in the figure.
Auto-ID plans to develop the EPC system into a global standard, which mainly includes: identifying the target specific code (EPC); defining the owner of the data (EPC manager); defining the remaining information of the code and the tag; defining the cargo parameters, such as Inventory unit number; Convert EPC code to Internet address (target naming service ONS); Describe the target (physical markup language PML); Gather and process RFID data (expert software); Specific number assigned to each type of target (string Line number); The minimum set of specifications (markers and identification specifications) for interoperability.
The biggest advantage of using RFID technology is that it can transparently manage the company's supply chain and effectively reduce costs. At present, many users are interested in using this technology to track various products, indicating that they plan to use RFID to track the internal assets of the company; there are many companies that will use this technology for logistics management.